MVNO Types & Operational Models Explained
- October 31, 2024
- Posted by: Allan Rasmussen
- Category: MVNO Academy
Types of mobile virtual network operators (MVNO) and their operational models
What are the various mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) models, such as Thin MVNO, Medium and Full MVNO – and what are the benefits/disadvantages of these models?
You will come across several names for the various types of MVNOs – or as a combination of types i.e.:
Airtime Reseller, Basic MVNO, Branded Reseller, Digital virtual network operators (DVNOs), Enhanced Service Provider (ESP), Extended MVNO, Full Mono IMSI MVNO, Full MVNO, Hybrid MVNO, IN MVNO, Medium MVNO, OMV, On-brand MVNO, Reseller MVNO, Service Provider MVNO, Sub-brand MVNO, Thick MVNO, Thin MVNO, VNO, IoT-VNO.
However the four most common used terms for MVNO definitions are:
- Reseller MVNO (Branded Reseller),
- Thin MVNO (Service Provider MVNO),
- Medium MVNO (Enhanced Service Provider MVNO),
- Full MVNO
MVNO Operational Models
MVNO types, such as branded reseller, service provider, thin, medium or full MVNO, etc., are largely defined by which of the operational components, network elements or facilities the MVNO manages and which one the hosting mobile network operator (MNO) manages – indicating the depth of the individual MVNO’s market participation.
Table: MVNO/MNO Operational Components
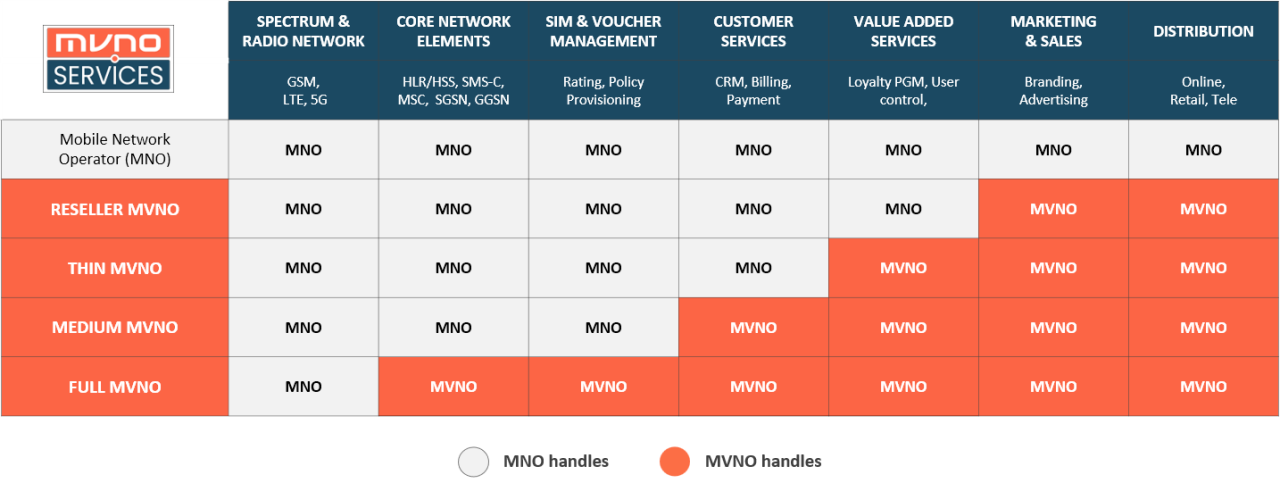
What is a Reseller MVNO?

A reseller MVNO (Branded Reseller), will either operate under its own brand or co-branded with the mobile network operator (MNO).
In most cases, the branded reseller brings a brand, distribution channels and/or a large existing customer base to the table, from which it can leverage its sales.
It is often the easiest MVNO type for a host network operator (HNO) to accept, as the HNO stays in control over most of the processes.
The Reseller MVNO, possesses no core elements and only holds the means that ensure the contact and relationship with the customers.
Advantages/Disadvantages of the Reseller MVNO model
Advantages
- Time to market and low startup costs as no investment in MVNO infrastructure is needed, the mobile network operator (MNO) will handle most of it.
- Use the MVNO (telecom) to drive an uplift in the core business.
Disadvantages
- No control. Customers, user data, post-sale interaction, SIMs, and infrastructure belongs to the mobile network operator (MNO),who is also responsible for the setting of tariffs.
- Revenues from incoming traffic (Interconnection) belongs to the MNO.
- The brand may not translate well to mobile
- The branded reseller may have an interest in more control but often lack in telecom experience.
- Taking share from the other established mobile network operators and MVNOs in the market is difficult without a solid understanding of the mobile industry and economics.
Operational Model / MVNO Architecture: Reseller MVNO
The Reseller MVNO is primarily only responsible for the costs of marketing, sales, and distribution.
Reseller MVNO Business Model
- Revenues: Revenue sharing with the mobile network operator (MNO). Typically, a certain gross margin over the existing retail offer from the MNO, and in some cases receive a commission per active subscriber acquired.
- Costs: Marketing, sales, distribution.
What is a Thin MVNO?

The Thin MVNO (Service provider MVNO), will operate under its own brand.
In best cases, the MVNO brings its own business concept, brand, distribution channels or a large existing customer base to the table, from which it can leverage its sales, or differentiate from the competition.
Advantages/Disadvantages of the Thin MVNO model
Advantages
- Self-owned SIMs, customer ownership and relationship is possible, as well as some ability to set tariff bundles and packages independently from the retail prices set by the host network operator, depending on the wholesale agreement.
- Use the MVNO to capture share in the mobile market and generate telecoms revenues -or to drive an uplift in the core business (bundles).
- Focus on addressing a particular niche or segment.
Disadvantages
- Less access and control: None, to very little user data access. Infrastructure belongs to the mobile network operator (MNO).
- Revenues from incoming traffic (Interconnection) often goes to the MNO.
- The Service Provider MVNO may have an interest in more control of the MVNO but often lack knowhow of the telecom experience.
- Costs on OPEX and CAPEX associated some IT platforms.
- May own the customers and SIMs, but not the International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI).
Operational Model / MVNO Architecture: Thin MVNO
The Thin MVNO (Service Provider MVNO), is normally responsible for the customer care processes, including the customer relationship management (CRM), support, billing processes and billing platform (BSS), tariffs, bundles and promotion packages, costs of marketing, sales, and distribution, as well as the OPEX and CAPEX associated with the IT platforms.
Thin MVNO Business Model
- Revenues: From traffic of its own customers (owns the customers, but not the IMSI’s).
- Costs: Wholesale rates, marketing, sales, distribution, OPEX/CAPEX associated to the IT platforms.
- Wholesale rates may vary with the type of Voice/Data/SMS/MMS e.g. On Net or Off Net, National or International (Origin/destination).
- Revenues from incoming traffic (Off Net) would typically belongs to the host network operator (HNO). In some cases, revenue might be shared with the HNO, i.e. a certain gross margin over the existing retail price offer from the HNO.
What is a Medium MVNO?

The Medium MVNO (Enhanced Service Provider MVNO), operates under its own brand with its own SIM cards, and can obtain its own numbering range/mobile network code.
Although not completely independent from the host operator, the MVNO can add its own value added services, to leverage sales, or differentiate from the competition.
Advantages/Disadvantages of the Medium MVNO model
Advantages
- Self-owned SIMs, Customer ownership and relationship, as well as the ability to set tariff bundles and packages independently from the retail prices set by the mobile network operator (MNO).
- Use the MVNO to capture share in the mobile market and generate telecoms revenues -or to drive an uplift in the core business (bundles).
- Focus on addressing a particular niche or segment.
- The MVNO can add its own value added services (VAS) platform to upsell or differentiate from the competition, on apps, data, and content services.
Disadvantages
- Costs on OPEX and CAPEX associated with IT platforms.
- Interconnect and IMSI comes from and is controlled by the mobile network operator (MNO).
- The MVNO cannot negotiate traffic wholesale interconnection agreements with other operators.
Operational Model / MVNO Architecture : Medium MVNO
- A Medium MVNO (Enhanced Service Provider), is responsible for the customer care processes, including the customer relationship management (CRM), support, billing processes and billing platform (BSS), tariffs, bundles and promotion packages, costs of marketing, sales, and distribution, as well as the OPEX and CAPEX associated with the IT platforms.
- Some may own their own home location register (HLR), which allows control of the Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number (MSISDN) which is a number used to identify a mobile phone number internationally.
Medium MVNO Business Model
- Revenues: From traffic of its own customers (owns the customers).
- Costs: Wholesale rates, marketing, sales, distribution, OPEX and CAPEX associated to the IT platforms.
- Wholesale rates may vary with the type of Voice/Data/SMS/MMS e.g. On Net or Off Net, National or International (Origin/destination).
What is a Full MVNO?

The Full MVNO is responsible for the whole operation, customers and data – giving it full control over all the services and products it offers in the market, as well as flexibility in designing and deploying new services, either to end-users or for Internet of Things (IoT) / Machine-to-machine (M2M).
The mobile network operator (MNO) supplies the network access.
The Full MVNO has a switching and transmission infrastructure allowing the management of its traffic. It can administer numbering resources, customer service, VAS, Roaming, SIM and device management and other services required for the provision of mobile services. This type of integration allows greater flexibility when using the capacity and services of mobile network operators
The Full MVNO operates (technically, not businesswise) in a similar way to a mobile network operator, but without spectrum and radio access network (RAN) which it still leases access to from a mobile network operator (MNO).
The amount of control and ownership over its business, its positioning, branding, marketing and the relationship a MVNO establishes and builds with its host operator are key factors for MVNOs success.
A Full MVNO delivers the most long term value to the host network operator.
Advantages/Disadvantages of the Full MVNO model
Advantages
- Its own SIM cards,
- Own numbering ranges,
- Home Location Register (HLR),
- Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN),
- Short Message Service Centre (SMSC),
- Multimedia Messaging Service (MMSC),
- Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC),
- Own roaming and interconnect agreements,
- Owning the network-switching infrastructure,
- Set tariff bundles and packages independently,
- Complete customer ownership and relationship,
- Focus on addressing a particular niche or segment,
- Upsell own or partner services as value added services (VAS),
- Access to big data (user usage data) to better address the needs and wants,
- Use the MVNO to capture share in the mobile market and generate telecoms revenues,
- Uplift to an existing core business (bundles) and obtain more control and independency from telcos.
Disadvantages
- Heavy (on-going) costs on OPEX and CAPEX associated with the needed IT platforms.
- Needs a high level of telecom and technology skills and knowhow.
Operational Model / MVNO Architecture : Full MVNO
- Responsible for all the whole infrastructure and value chain – except network radio and spectrum.
Table: Example of Elements, Functions and their advantage to the Full MVNO
| Elements | Function | Advantages |
| MSC Mobile Switching Center |
|
|
| SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node |
|
|
| GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node |
|
|
| HLR Home Location Register |
|
|
In a Full MVNO stack integration example, the Full MVNO will install Business and Operations Support Systems (BSS/OSS) and Core Elements such as:
- IN (SCP)
- STP/DSC
- HLR/HSS
- SBC
- SMSC/SMS-G
- IVR/VMS
- OSS/BSS
- OCS
- GGSN/PGW
- USSDGW
The hosting mobile network operator (MNO) is responsible for providing the following network elements:
- Radio Access Network
- MME/SGW/SGSN/GGSN/PGW/PCRF
- MSC/VLR/STP/EIR
- EIR (MNO/MVNO)
- SBC/GMSC
- DRA (DSC)
- Internet (ISP)
- DNS
- Public IPs and NAT
Full MVNO Business Model
- Revenues: From traffic of its own customers, bundle offers and revenues from incoming traffic (Off Net)
- Costs: Wholesale rates, marketing, sales, distribution, heavy OPEX and CAPEX associated to the IT platforms.
The Full MVNO can:
- Have their own roaming and interconnect agreements with other mobile network operators.
Gain deep insights into customer or machine (M2M/IoT) profile. - Create “stickiness” with customers, where the customer will be under greater control of the MVNO.
- Offer a convergence proposition, where the technical integration is important.
- Operating as a Full MVNO, provides the MVNO the opportunity to increase its focus on differentiation, segmentation and customer loyalty.
ประเภทของผู้ให้บริการ MVNO
ผู้ให้บริการ MVNO สามารถแบ่งออกเป็น 5 ประเภท ตามระดับความเป็นเจ้าของและการควบคุมบริการ ดังนี้:
Reseller MVNO
ทำหน้าที่เป็นเพียงตัวแทนจำหน่ายบริการจากผู้ให้บริการ MNO (Mobile Network Operator) หรือจากผู้ให้บริการขายส่งบริการโทรศัพท์เคลื่อนที่ (Mobile Virtual Network Aggregators: MVNA) โดยไม่ได้ลงทุนในโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน โครงข่าย หรือระบบของตนเอง ลักษณะนี้เหมาะสำหรับผู้เริ่มต้นธุรกิจ เนื่องจากมีความเสี่ยงและต้นทุนต่ำ
Branded Reseller MVNO
นำบริการที่ซื้อจากผู้ให้บริการ MNO หรือ MVNA มาสร้างแบรนด์และทำการตลาดในนามของตนเอง โดยเน้นการสร้างความแตกต่างผ่านการตลาดและภาพลักษณ์
Thin MVNO
ลงทุนในระบบที่จำเป็น เช่น ระบบบิลลิ่ง (Billing) และการจัดการลูกค้าสัมพันธ์ (CRM) ซื้อบริการแบบขายส่ง (Wholesale) จาก MNO หรือ MVNA ควบคุมการออกแบบแพ็กเกจและกลยุทธ์การตลาด เหมาะสำหรับผู้ที่มีความเชี่ยวชาญในธุรกิจโทรคมนาคม
Enhanced MVNO (Medium MVNO)
ลงทุนในระบบที่ครบถ้วนยิ่งขึ้น เช่น ระบบบิลลิ่ง, CRM และบริการเสริมมูลค่า (Value Added Services: VAS) ควบคุมทุกส่วนตั้งแต่การออกแบบแพ็กเกจ การพัฒนาแอปพลิเคชัน การทำการตลาด ไปจนถึงการดูแลและให้บริการลูกค้า
Full MVNO
มีโครงสร้างการดำเนินธุรกิจที่ใกล้เคียงกับ MNO แต่ไม่มีโครงข่ายการเข้าถึงและคลื่นความถี่เป็นของตนเอง สามารถควบคุมบริการและผลิตภัณฑ์ทั้งหมดได้ รวมถึงการออกแบบบริการใหม่ การบริหารจัดการโครงสร้างพื้นฐานบางส่วน และการดูแลลูกค้าอย่างเต็มรูปแบบ
Latest Post
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator (MVNA) and Its Role in the MVNO Ecosystem?
What is a Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator (MVNA), and what role does it play in the MVNA, MVNE, MVNO, MNO ecosystem?
November 14, 2024Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) | Official Definitions
Discover the official definitions of a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) from various regulatory authorities and what a MVNO actually is
October 30, 202410 Key Factors for MVNO Success Explained: A Comprehensive Guide
What is actually needed to make a mobile virtual network operator (MVNO) successful? Here are 10 key factors for MVNO success explained.
July 1, 2024



